Controlling Model Railway with FlashAir GPIO
Contributor: ayase hiro
Latest update: March 2016
Overview
The High/Low input of Arduino's digital I/O is driven by the FlashAir's GPIO H/L output. Another digital I/O
pin of the Arduino
will act as a PWM output to the drive motor of model railway vehicle through a full-bridge driver.
We can also control the electromagnet at the switch point through a full-bridge driver.
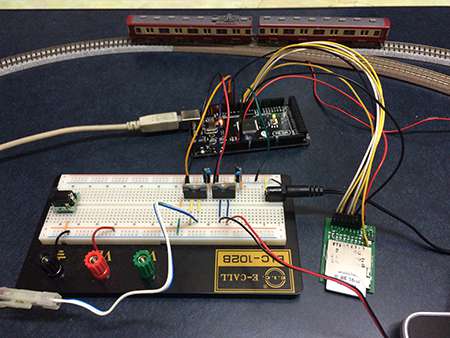
Details
FlashAir CONFIG setting
To enable the GPIO of FlashAir, add 「IFMODE=1」 to the CONFIG file of SD_WLAN in a folder in the FlashAir.
ref. IFMODEof command.cgi
Connect FlashAir and Arduino
The GPIO terminal of the FlashAir is connected to the digital I/O pins of the Arduino.
| Bit Assignment | FlashAir | Arduino |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01 | CMD | digital I/O pin No.2(D2) |
| 0x02 | D0 | digital I/O pin No.3(D3) |
| 0x04 | D1 | digital I/O pin No.4(D4) |
| 0x08 | D2 | digital I/O pin No.5(D5) |
| 0x10 | D3 | digital I/O pin No.6(D6) |
In order to use an SD Card with Arudino, we used a SDcard DIP module from Akizuki .
ref. Akizuki SDcard DIP module

FlashAir in SD card slot DIP module
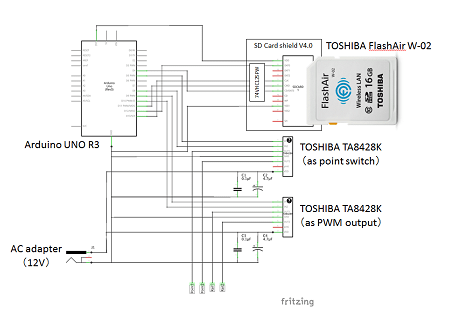
Full circuit diagram
GPIO output of FlashAir
From a browser that can connect to the to FlashAir you can pass GPIO commands by accessing the appropriate URL
such
as
http://flashair/command.cgi?op=190&CTRL=0x1f&DATA=0xXX, which set H/L output of GPIO pins. To make
this less
combersome, I made a JavaScript HTML file List.htm and put it on the FlashAir which has buttons a user can press
to
set the GPIO register and thus train operations accordingly.
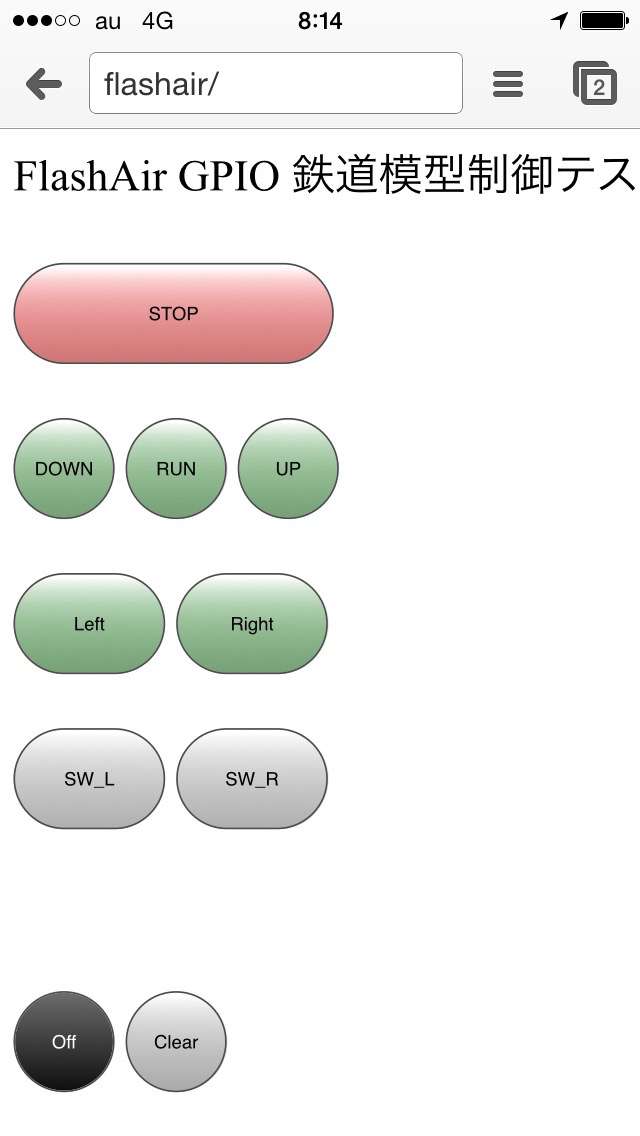
List.htm displayed on the iPhone
| Button | Behavior and Roles |
|---|---|
| STOP | Emergency stop button. Such as when the vehicle model train was derailed, in order to stop immediately. |
| DOWN | Slow down. Arduino drops speed gradually at once pressed down. |
| RUN | To maintain the current speed. |
| UP | Speed up. Arduino increases the speed gradually at once pressed down. |
| Left | Switch the running direction to the left. |
| Right | Switch the running direction to the right. |
| SW_L | Switch Point( rail open direction ) to the left. |
| SW_R | Switch Point( rail open direction ) to the right. |
| Off | All of the GPIO to Low. |
| Clear | To reload the screen. |
JavaScript for Train Operation Webpage
<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript"> <!—
//Function:HTTP communication to FlashAir
function flashair_get( param ){
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open("GET", param, false);
request.send(null);
}
//Global variable definition
var send_mess = "http://flashair/command.cgi?op=190&CTRL=0x1f&DATA=0x";
var p = 0x00;
//Function:to any port in the H/L
function gpio_onoff(port){
switch( port ){
case 1: //Emergency stop
p |= 0x01;
document.getElementById('RUN_STOP').style.backgroundColor = '#aa0000';
url = send_mess + p.toString(16);
flashair_get(url);
break;
case 20: //point control High: opposite direction
(approx.)
case 21: //point control Low: default direction
(approx.)
case 30: //running direction High: right
(approx.)
case 31: //running direction Low: left
(approx.)
case 4: //running control High: speed up
(approx.)
case 5: //running control High: slow down
(approx.)
case 6: //running control Low: coasting
(approx.)
}
document.getElementById('RESULT').value = p.toString(16);
}
//-->
</script>
Definition of GPIO input status and behavior
In this case, five operations shown in the following table has been achieved so as to correspond to each GPIO. The operation when each GPIO has become HIGH defined as shown in the table below.In the case all of the GPIO is LOW, it has to maintain the current status( speed and direction ).
| Bit Assignment | FlashAir | HIGH/LOW | Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01 | CMD | HIGH | Running stop of the model railway vehicle |
| 0x02 | D0 | HIGH | To switch the direction of the point to the left. |
| LOW | To switch the direction of the point to the right. | ||
| 0x04 | D1 | HIGH | To the running direction of the railway model vehicle to the left. |
| LOW | To the running direction of the railway model vehicle to the right. | ||
| 0x08 | D2 | HIGH | Increase the running speed of the railway model vehicle.(speed up) |
| 0x10 | D3 | HIGH | Reducing the running speed of the model railroad vehicle.(slow down) |
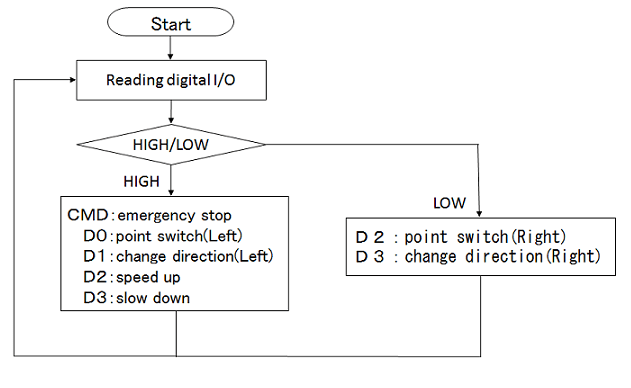
Arduino Flowchart
Check GPIO input status on the Arduino
In Arduino, always check the GPIO input status of FlashAir in a loop function. Check the status of No.2~6 pins of H/L of digital I/O, so that you designated operation is performed.
const int sdcard_gpio_pin[5] = { 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
const int sdcard_gpio_pin_num = 5;
void loop() {
for(int idx=0; idx < sdcard_gpio_pin_num; idx++)
{
if(digitalRead(sdcard_gpio_pin[idx]) == HIGH){
if(idx == 0){
funcspeed_stop();
status_stop = 1;
}
else if(idx == 1){
pointswitch(1);
}
else if(idx == 2){
if(status_LR != 1){
status_LR = 1;
}
}
else if(idx == 3){
funcspeed(0); //slow down
}
else if(idx == 4){
funcspeed(1); //speed up
}
}
else{
if(idx == 0){
status_stop = 0;
}
else if(idx == 1){
pointswitch(0);
}
else if(idx == 2){
if(status_LR != 0){
status_LR = 0;
}
}
}
}
}
Let's Get Moving
The output of the full-bridge driver for the PWM output that is connected to the railway input and the output of the full-bridge driver for point conversion to connected to that point. We are using a Kato Precision Railroad Models (KATO) set but you can connect other sets in the same way, such as Tommy Tech (TOMIX).
In the photo, a personal computer is connected for debugging with the serial monitor, it is not needed for the operation of the model railway. In addition, the iPad connected to the FlashAir displaying the operation web page described above.
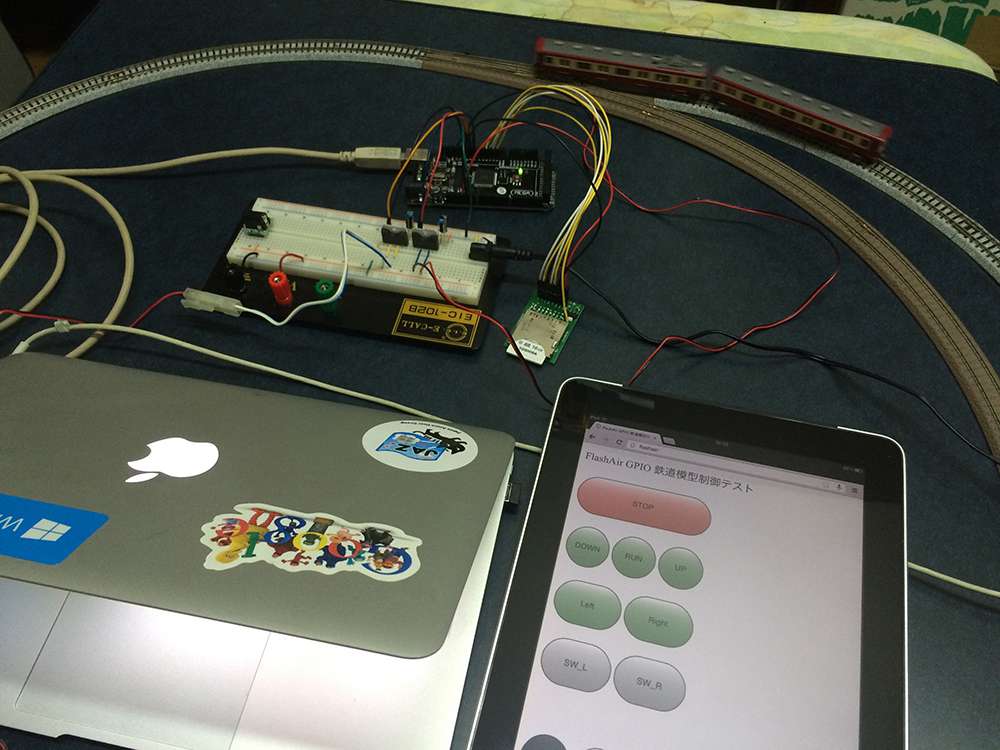

Operating the model train with a FlashAir can be seen in this video:
Conclusion
In this case you can operate the model railway as driving the motor by the PWM output of the Arduino. For example, it would also be possible to operate a model car with a FlashAir.
For all inquiries, please contact to the author.
 FlashAir™ Developers
FlashAir™ Developers